Cloud Services
- Don't be overwhelmed with managing your IT infrastructure
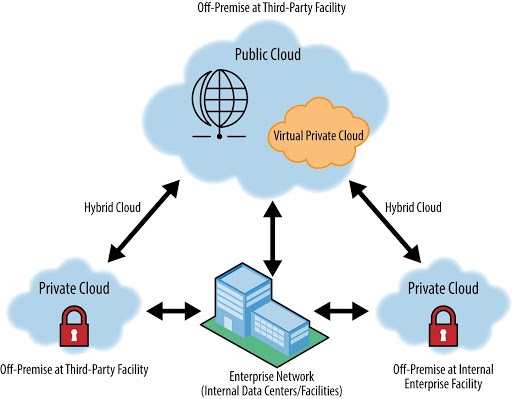
With an extensive experience of deploying private cloud networks for our customers for many years, BTC has also implemented many hybrid and multi-cloud projects thereby giving the client to have flexibility to have its critical applications on premises in a private could and rolling out dynamic and less critical applications on public clouds on any cloud platform to have the ability to immediately respond to the requirements of the application whenever traffic, compute resources demand increases and vice versa.
A multi-cloud platform option provides the best services that each platform offers, this allows companies to customize & minimize the infrastructure that is specific to their business goals.
Types of Cloud